Your Clinic
SET A LOCATION
Your Clinic
SET A LOCATION
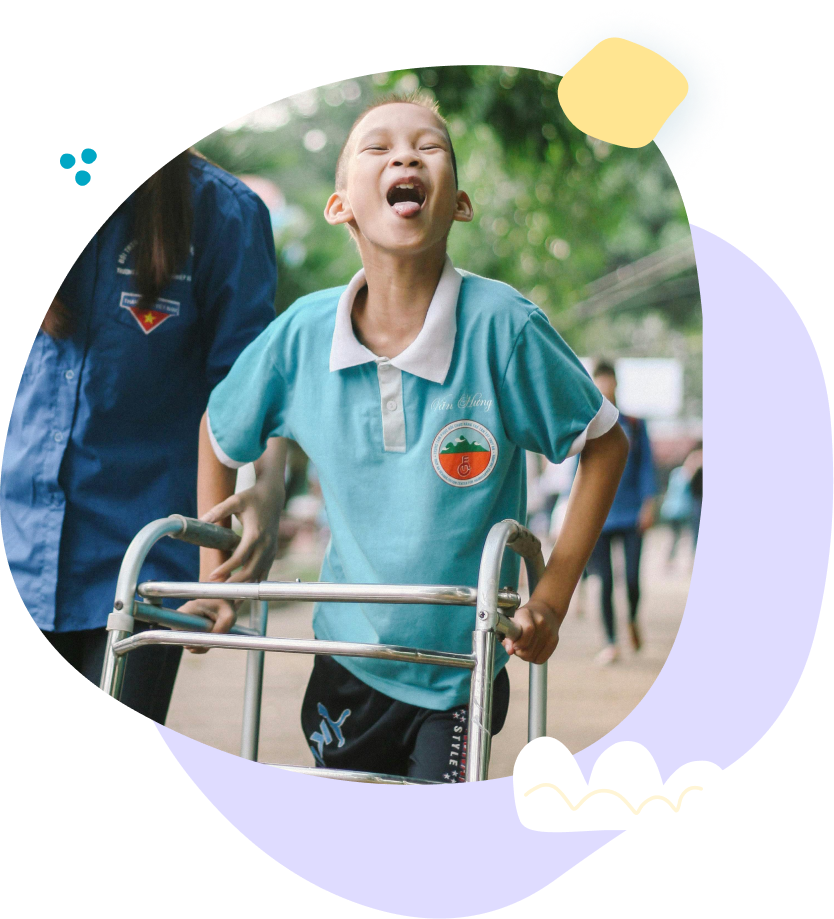
Muscular dystrophy (MD) refers to a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. Affecting children globally, this condition often requires ongoing support to manage its impact on mobility and daily life.
Understanding the types of muscular dystrophy helps families and caregivers prepare for effective interventions. Common types include:
Progressive Pediatric Therapy provides a comprehensive range of therapeutic tools specifically adapted for children with muscular dystrophy. Our interventions focus on maintaining function, managing progressive changes, and supporting quality of life.

Aquatic Therapy is a skilled treatment method used by therapists to enhance your child's functional abilities. The warm, buoyant water enables your child to feel free and have fun in therapy, in a natural environment! The water's buoyancy reduces stress on joints and muscles while providing resistance for strength building, making it particularly beneficial for children with movement limitations.
Attend our clinics for expert orthotics evaluations and fittings, designed to improve mobility and ensure optimal comfort tailored to your needs. Children at PPT can attend monthly clinics for custom wheelchairs or orthotics, designed to enhance mobility and ensure proper postural alignment. These specialized devices support proper body alignment and improve functional mobility.
PPT uses cutting-edge tools like Galileo whole-body vibration platforms and Mano dumbbells to enhance therapy outcomes. Therapeutic vibration helps to optimize neuroplasticity, promote motor learning and decrease the complications of many childhood conditions that limit movement, sensory processing skills, and learning. A unique therapeutic intervention used to decrease muscle tightness, change habitual patterns of movement in a single joint, or improve range of motion.
The Turtle Brace is a specialized orthotic device designed to provide targeted support and positioning for children with specific postural or alignment needs. This custom-fitted brace helps maintain proper body positioning and supports therapeutic goals related to posture, movement patterns, and functional positioning during activities.
For children with muscular dystrophy, therapies play a crucial role in enhancing quality of life. Both occupational therapy (OT) and physical therapy (PT) offer tailored strategies to manage symptoms, improve mobility, and promote independence.

Physical therapy (PT) aims to maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and mobility through:
Preventing contractures and maintaining
joint function.
Techniques to enhance lung capacity and breathing efficiency.
Supporting walking or transitioning to mobility aids.
Occupational therapists help children navigate daily activities by focusing on:
Strengthening small muscles for tasks like writing or self-feeding
Introducing tools such as specialized utensils, wheelchairs, or braces.
Modifying environments to ensure accessibility and safety.

Starting therapy early can significantly slow the progression of muscular dystrophy symptoms. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, therapists, and families create a supportive network, allowing children to achieve their fullest potential.
While muscular dystrophy presents challenges, occupational and physical therapies offer essential support to improve daily living and foster independence. If your child has been diagnosed with muscular dystrophy, consult specialists to develop a customized therapy plan that meets their needs
Explore resources and expert guidance on managing muscular dystrophy effectively Schedule an evaluation to connect with our team of specialists today
We empower children, families, and the community to learn, grow, and celebrate every child's unique abilities.
Quick Links
Contact Details
Phone: 561-376-2573 | 561-918-0190
Fax: 561-218-4939
VIP Concierge: 561-717-1764
Clinic Locations
All Rights Reserved | Progressive Pediatric Therapy, Inc. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service
Site by Spearlance