Your Clinic
SET A LOCATION
Your Clinic
SET A LOCATION
Hypotonia, also known as low muscle tone, is a condition that affects muscle strength and control. In children, hypotonia can manifest as delayed milestones, such as difficulty sitting, crawling, or walking, and challenges with posture and coordination.
Parents and caregivers might notice symptoms such as:
Floppy or "ragdoll-like" appearance of limbs
Poor head control
Difficulty feeding or swallowing
Delayed motor skills
Fatigue during physical activities
These challenges can impact a child's overall development, but with the right interventions, significant progress is possible.
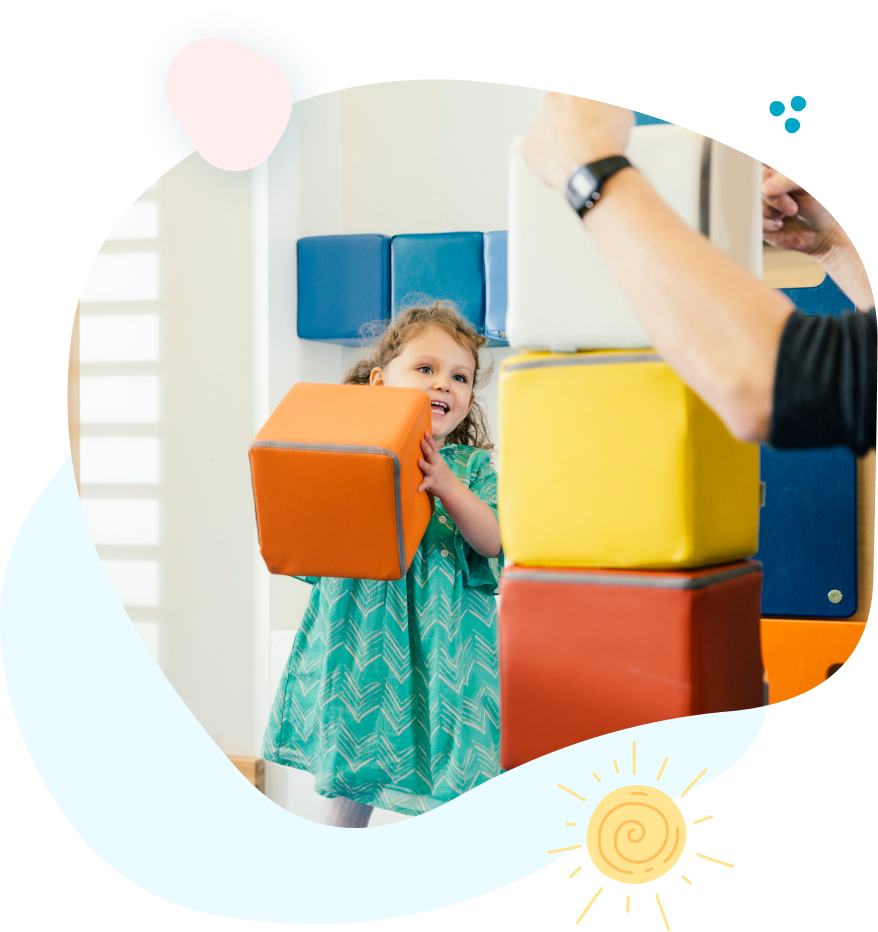

Our specialized tools address the unique challenges of low muscle tone, helping children build strength, stability, and endurance. These interventions support improved posture, motor control, and functional abilities in children with hypotonia.

Aquatic Therapy is a skilled treatment method used by therapists to enhance your child's functional abilities. The warm, buoyant water enables your child to feel free and have fun in therapy, in a natural environment! The water's buoyancy reduces stress on joints and muscles while providing resistance for strength building, making it particularly beneficial for children with movement limitations.
Attend our clinics for expert orthotics evaluations and fittings, designed to improve mobility and ensure optimal comfort tailored to your needs. Children at PPT can attend monthly clinics for custom wheelchairs or orthotics, designed to enhance mobility and ensure proper postural alignment. These specialized devices support proper body alignment and improve functional mobility.
PPT uses cutting-edge tools like Galileo whole-body vibration platforms and Mano dumbbells to enhance therapy outcomes. Therapeutic vibration helps to optimize neuroplasticity, promote motor learning and decrease the complications of many childhood conditions that limit movement, sensory processing skills, and learning. A unique therapeutic intervention used to decrease muscle tightness, change habitual patterns of movement in a single joint, or improve range of motion.
A multidisciplinary approach is often the most effective for managing hypotonia in children. Occupational, physical, and speech therapy each play unique roles in fostering a child’s development.
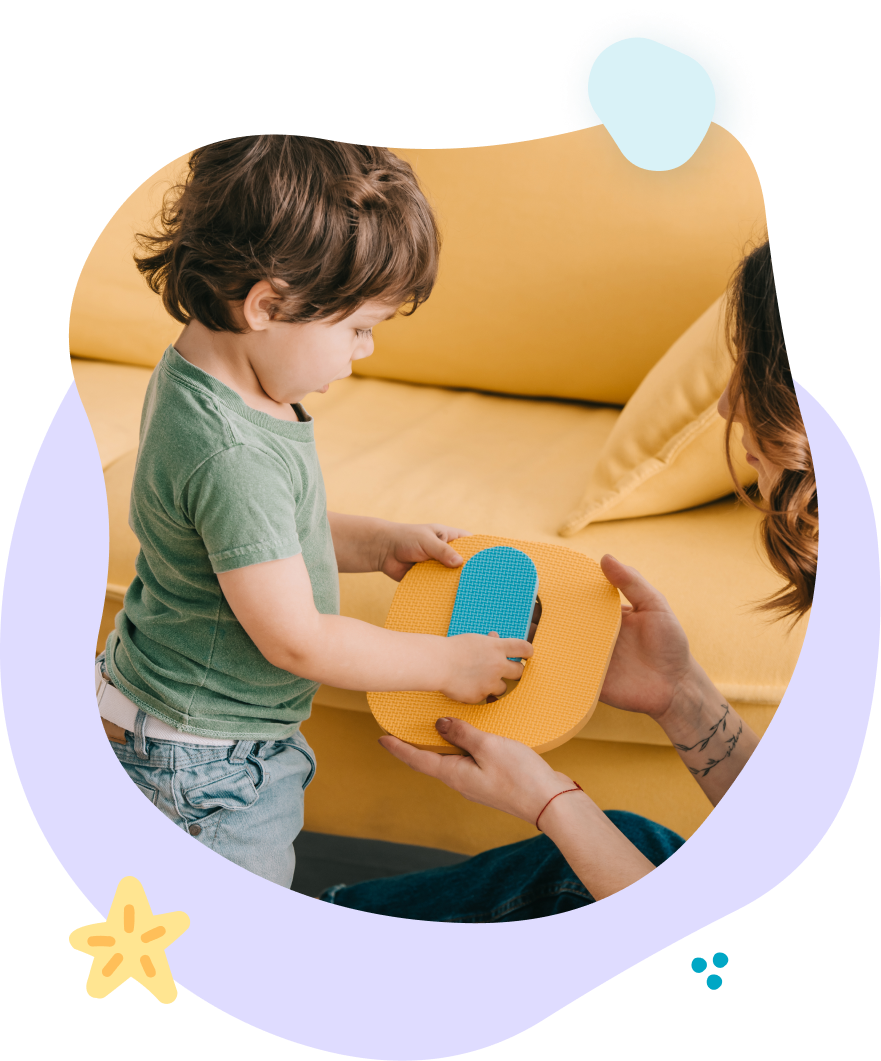

Occupational therapy (OT) focuses on helping children with hypotonia achieve independence in daily activities. Therapists work to improve fine motor skills, coordination, and strength through tailored exercises and play-based interventions.
Activities include:
Floppy or "ragdoll-like" appearance of limbs
Practicing self-care tasks like dressing and feeding
Strengthening core muscles for posture and stability
By improving functional abilities, OT helps children build confidence and participate actively in their environments.
Physical therapy (PT) targets gross motor skills, mobility, and overall muscle strength. PT is crucial for children with hypotonia who struggle with physical activities like standing, walking, or jumping.
Therapeutic methods include:
Balance and coordination exercises
Core and limb strengthening routines
Stretching to reduce joint laxity
With consistent physical therapy (PT), children can develop better muscle control, making everyday movements easier and more efficient.
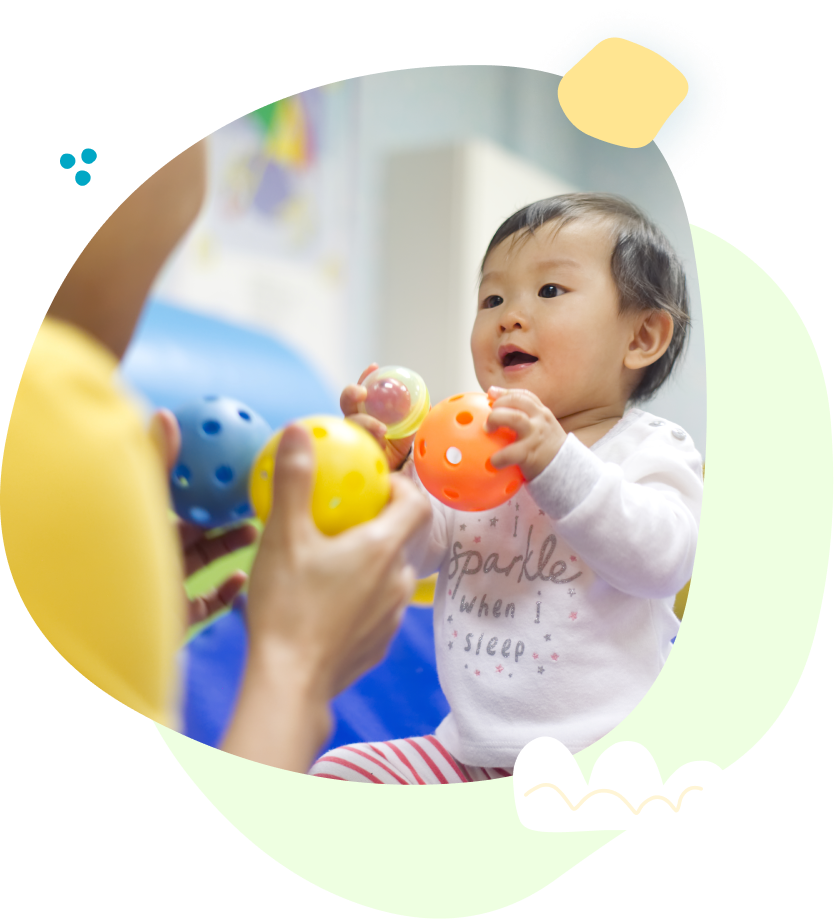
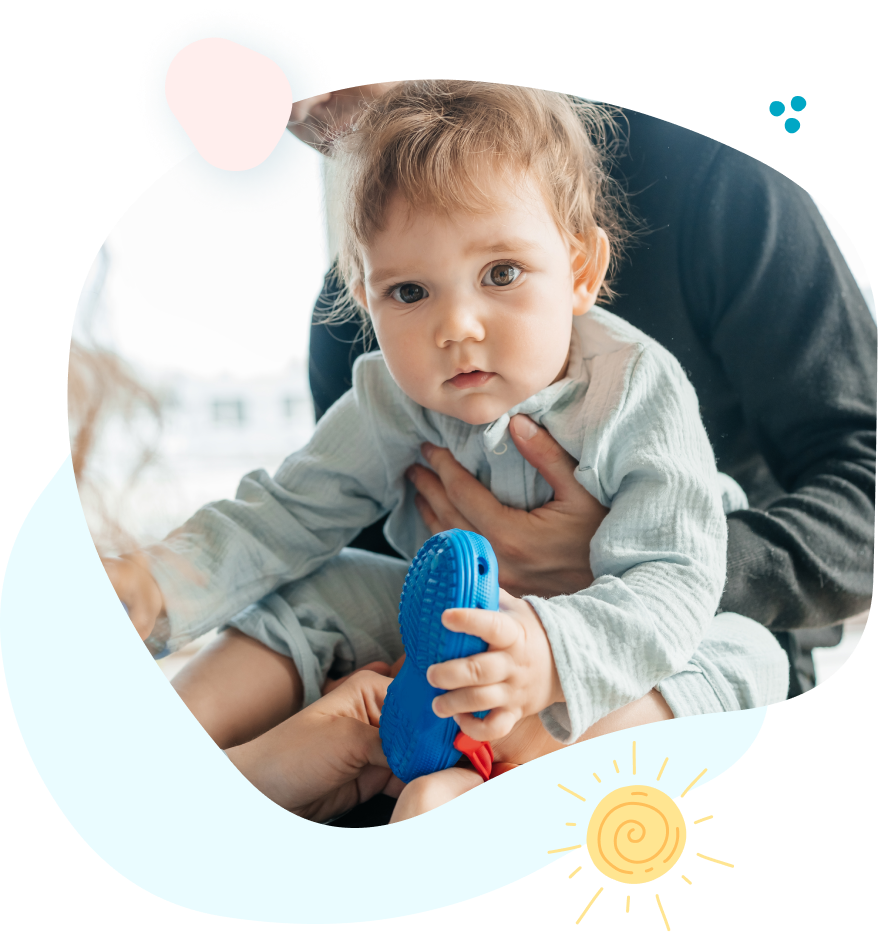


Hypotonia can also affect oral muscles, leading to difficulties with speech and feeding. Speech therapists address these challenges by strengthening the muscles used for talking, chewing, and swallowing.
Therapeutic approaches include:
Oral-motor exercises to improve feeding abilities
Language development activities to enhance communication
Techniques to support clearer speech production
These interventions not only aid in communication but also promote social engagement and self-expression.
Parental involvement is key to maximizing the benefits of therapy. Families can:
Reinforce therapy techniques at home
Celebrate small milestones to encourage progress
Work closely with therapists to tailor strategies to the child’s unique needs
Early intervention is critical in addressing hypotonia. The earlier therapy begins, the more opportunities a child has to build foundational skills and adapt to challenges. Therapy can be life-changing, empowering children to reach their full potential.
If you’re concerned about your child’s muscle tone or developmental progress, contact us to schedule an evaluation. Our team of occupational, physical, and speech therapists is here to help your child thrive.
Contact us to learn more about our personalized therapy programs for children with hypotonia.
We empower children, families, and the community to learn, grow, and celebrate every child's unique abilities.
Quick Links
Contact Details
Phone: 561-376-2573 | 561-918-0190
Fax: 561-218-4939
VIP Concierge: 561-717-1764
Clinic Locations
All Rights Reserved | Progressive Pediatric Therapy, Inc. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service
Site by Spearlance