Your Clinic
SET A LOCATION
Your Clinic
SET A LOCATION
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that originates from the spinal cord and controls movement and sensation in the shoulders, arms, and hands. When this network is injured, it can result in varying degrees of impairment in motor skills and sensation, especially for infants and children who rely on these nerves for early developmental milestones.
Brachial plexus injuries (BPIs) occur when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or torn. In infants, such injuries often happen during childbirth, particularly in cases of complicated deliveries, breech births, or when excessive force is applied. In children, these injuries may result from trauma, such as accidents or sports injuries.
Weakness or immobility in the affected arm
Loss of sensation
Poor grip strength
Difficulty in performing fine motor skills
The severity can range from temporary weakness (neuropraxia) to more severe forms like nerve root avulsion.
Children recovering from brachial plexus injuries receive targeted therapeutic interventions designed to restore strength, mobility, and function to the affected arm. Our specialized tools help retrain neural pathways and rebuild motor control.

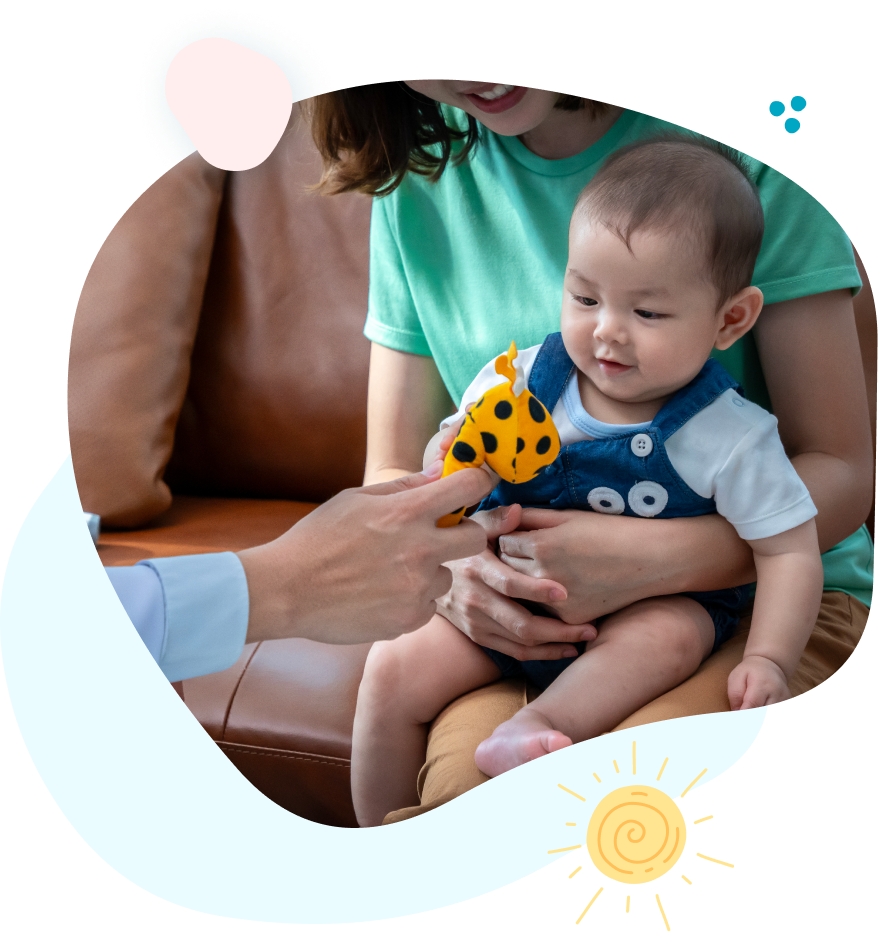
Aquatic Therapy is a skilled treatment method used by therapists to enhance your child's functional abilities. The warm, buoyant water enables your child to feel free and have fun in therapy, in a natural environment! The water's buoyancy reduces stress on joints and muscles while providing resistance for strength building, making it particularly beneficial for children with movement limitations.
PPT uses cutting-edge tools like Galileo whole-body vibration platforms and Mano dumbbells to enhance therapy outcomes. Therapeutic vibration helps to optimize neuroplasticity, promote motor learning and decrease the complications of many childhood conditions that limit movement, sensory processing skills, and learning. A unique therapeutic intervention used to decrease muscle tightness, change habitual patterns of movement in a single joint, or improve range of motion.
Recovery and rehabilitation from a brachial plexus injury depend on early and effective intervention. Occupational therapy and physical therapy play a crucial role in helping children regain functionality, adapt to challenges, and achieve developmental milestones.

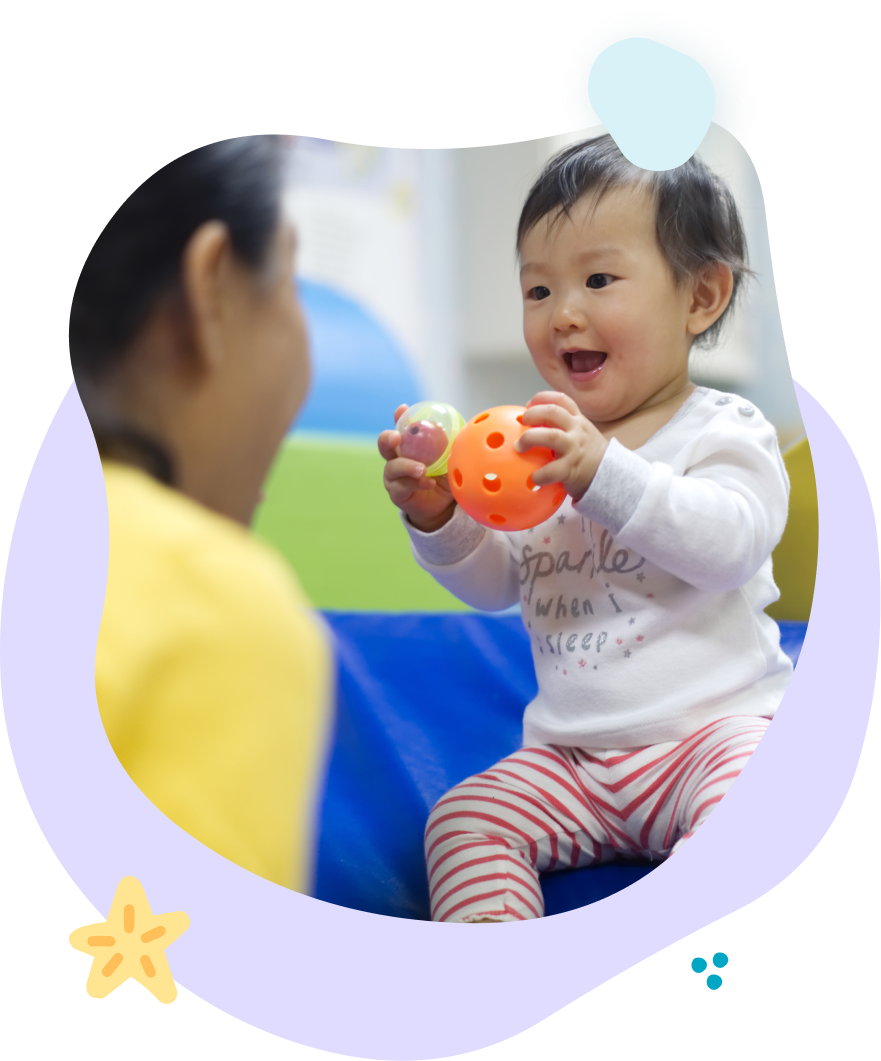
Occupational therapy focuses on improving the child's ability to perform daily activities, particularly those involving the use of the arms and hands. Key strategies include:
Activities like grasping toys, holding
utensils, and drawing help improve hand function and dexterity.
Custom orthotic devices may be used to
support the arm, reduce stiffness, and encourage proper positioning
for healing and growth.
For children experiencing numbness or
hypersensitivity, OTs use techniques to normalize sensory responses.
Occupational therapists also work closely with parents, teaching them exercises and modifications to support their child’s development at home.
Physical therapy aims to restore strength, mobility, and coordination in the affected arm. It complements OT by focusing on larger muscle groups and movements. Core components of PT include:
Gentle stretching and movements
prevent joint stiffness and contractures.
Therapists use age-appropriate tools like
resistance bands or soft weights to rebuild muscle strength.
For infants and toddlers, PT ensures they meet key milestones, such as crawling or reaching, which can be affected by the injury.

The most effective treatment plans combine OT and PT with other interventions like neurology consultations, surgical evaluations, and parent education. In severe cases, surgical repair of the nerve may be necessary, followed by intensive rehabilitation.
With early diagnosis and the support of skilled occupational and physical therapists, most children with brachial plexus injuries can achieve significant improvements. These therapies not only address physical recovery but also empower children to lead fulfilling lives, nurturing their confidence and independence.
If your child has been diagnosed with a brachial plexus injury, contact us to schedule an evaluation today to begin their journey toward recovery.
We empower children, families, and the community to learn, grow, and celebrate every child's unique abilities.
Quick Links
Contact Details
Phone: 561-376-2573 | 561-918-0190
Fax: 561-218-4939
VIP Concierge: 561-717-1764
Clinic Locations
All Rights Reserved | Progressive Pediatric Therapy, Inc. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service
Site by Spearlance